
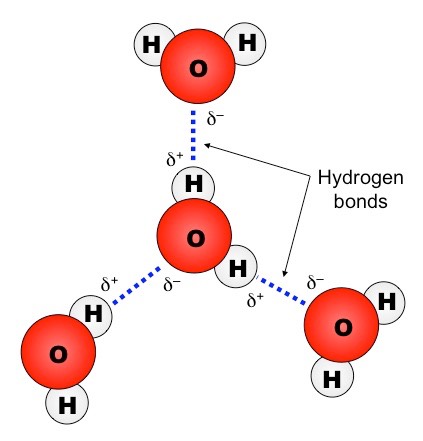

In 1783, French chemist Antoine Lavoisier 1743 –1794 gave the name hydrogen. However, Cavendish was often the one credited for discovering hydrogen for correctly assuming its elemental nature. Robert Boyle 1627 –1691, an Anglo-Irish chemist and regarded as the first modern chemist, was one of those who had done it earlier. He was not the first to have prepared hydrogen gas. He called the gas inflammable air and described it in his paper, “On Factitious Airs”. In 1766, British chemist, Henry Cavendish 1731 –1810, discovered hydrogen. Hydrocarbons are one of the chief organic compounds. Organic compounds are fundamentally defined as those substances containing carbon atoms and Carbon-Carbon (C-C) and Carbon-Hydrogen (C-H) bonds. Examples of biologically important inorganic compounds containing hydrogen are water (H 2O) and hydrochloric acid (HCl, which is produced by the stomach). Inorganic compounds are those substances that generally lack Carbon-Carbon (C-C) and Carbon-Hydrogen (C-H) bonds. Some of the common natural hydrides are ammonia (NH 3), ethane (C 2H 6), and methane (CH 4). Also, hydrogen that is bound to metals or metalloid is also called hydrides. It may also refer to a compound where hydrogen reacts with a more electropositive element or groups, forming a compound. A hydridepertains to the anion of the hydrogen, i.e.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
